https://www.worldhistorymaps.info/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/persia_500bc.jpg
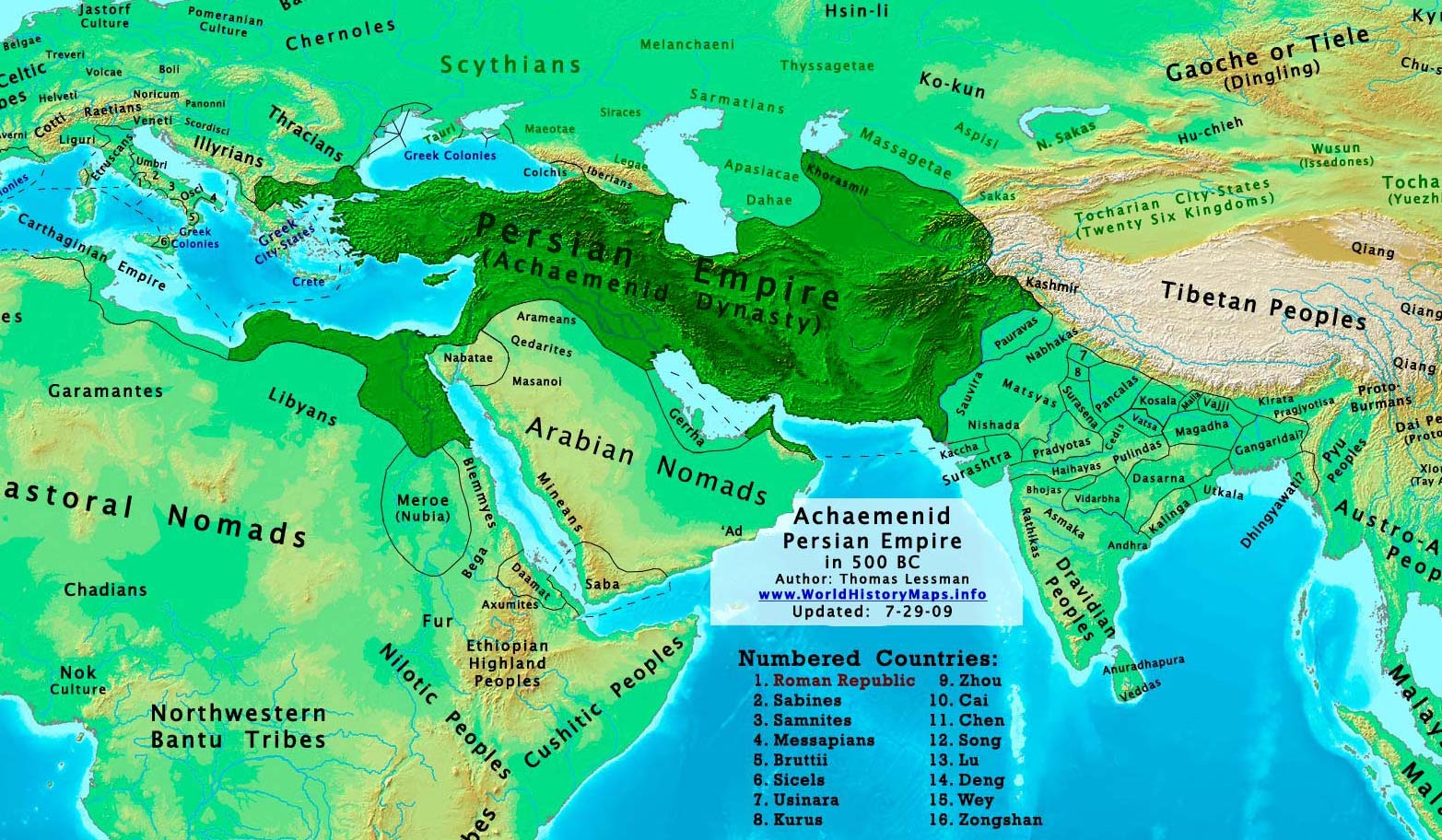
The Achaemenid Empire (/əˈkiːmənɪd/; romanized: Xšāça, lit. ‘The Empire’), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire based in Western Asia founded by Cyrus the Great. Ranging at its greatest extent from the Balkans and Eastern Europe proper in the west to the Indus Valley in the east, it was larger than any previous empire in history, spanning 5.5 million square kilometers (2.1 million square miles). It is notable for its successful model of a centralised, bureaucratic administration (through satraps under the King of Kings), for its multicultural policy, for building infrastructure such as road systems and a postal system, the use of an official language across its territories, and the development of civil services and a large professional army. The empire’s successes inspired similar systems in later empires.
By the 7th century BC, the Persians had settled in the south-western portion of the Iranian Plateau in the region of Persis, which came to be their heartland. From this region, Cyrus the Great advanced to defeat the Medes, Lydia, and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, establishing the Achaemenid Empire. Alexander the Great, an avid admirer of Cyrus the Great, conquered most of the empire by 330 BC. Upon Alexander’s death, most of the empire’s former territory fell under the rule of the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Seleucid Empire, in addition to other minor territories which gained independence at that time. The Iranian elites of the central plateau reclaimed power by the second century BC under the Parthian Empire.
Source: Wikipedia