https://www.worldhistorymaps.info/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/indo-greeks_100bc.jpg
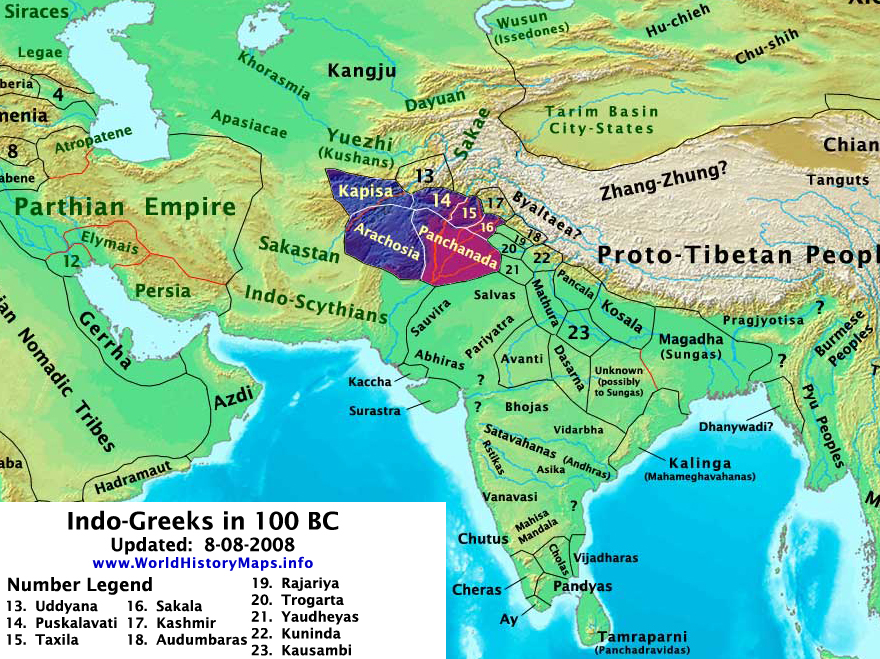
The Indo-Greek Kingdom or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, and historically known as Yavanarajya (Kingdom of Yavanas), was a Hellenistic kingdom spanning modern-day Afghanistan and the classical circumscriptions of the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent (northern Pakistan and northwestern India), which existed during the last two centuries BC and was ruled by more than thirty kings, often conflicting with one another.
The kingdom was founded when the Graeco-Bactrian king Demetrius invaded the subcontinent early in the 2nd century BC. The Greeks in the Indian Subcontinent were eventually divided from the Graeco-Bactrians centered on Bactria (now the border between Afghanistan and Uzbekistan), and the Indo-Greeks in the present-day north-western Indian Subcontinent. The most famous Indo-Greek ruler was Menander (Milinda). He had his capital at Sakala in the Punjab (present-day Sialkot).[citation needed]
The expression “Indo-Greek Kingdom” loosely describes a number of various dynastic polities, traditionally associated with a number of regional capitals like Taxila, (modern Punjab (Pakistan)), Pushkalavati and Sagala. Other potential centers are only hinted at; for instance, Ptolemy’s Geographia and the nomenclature of later kings suggest that a certain Theophila in the south of the Indo-Greek sphere of influence may also have been a satrapal or royal seat at one time.
During the two centuries of their rule, the Indo-Greek kings combined the Greek and Indian languages and symbols, as seen on their coins, and blended Greek and Indian ideas, as seen in the archaeological remains. The diffusion of Indo-Greek culture had consequences which are still felt today, particularly through the influence of Greco-Buddhist art. The ethnicity of the Indo-Greek may also have been hybrid to some degree. Euthydemus I was, according to Polybius, a Magnesian Greek. His son, Demetrius I, founder of the Indo-Greek kingdom, was therefore of Greek ethnicity at least by his father. A marriage treaty was arranged for the same Demetrius with a daughter of the Seleucid ruler Antiochus III. The ethnicity of later Indo-Greek rulers is sometimes less clear. For example, Artemidoros (80 BC) may have been of Indo-Scythian ascendency, although this is now disputed.
Following the death of Menander, most of his empire splintered and Indo-Greek influence was considerably reduced. Many new kingdoms and republics east of the Ravi River began to mint new coinage depicting military victories. The most prominent entities to form were the Yaudheya Republic, Arjunayanas, and the Audumbaras. The Yaudheyas and Arjunayanas both are said to have won “victory by the sword”. The Datta dynasty and Mitra dynasty soon followed in Mathura. The Indo-Greeks ultimately disappeared as a political entity around 10 AD following the invasions of the Indo-Scythians, although pockets of Greek populations probably remained for several centuries longer under the subsequent rule of the Indo-Parthians and Kushans.
Source: Wikipedia